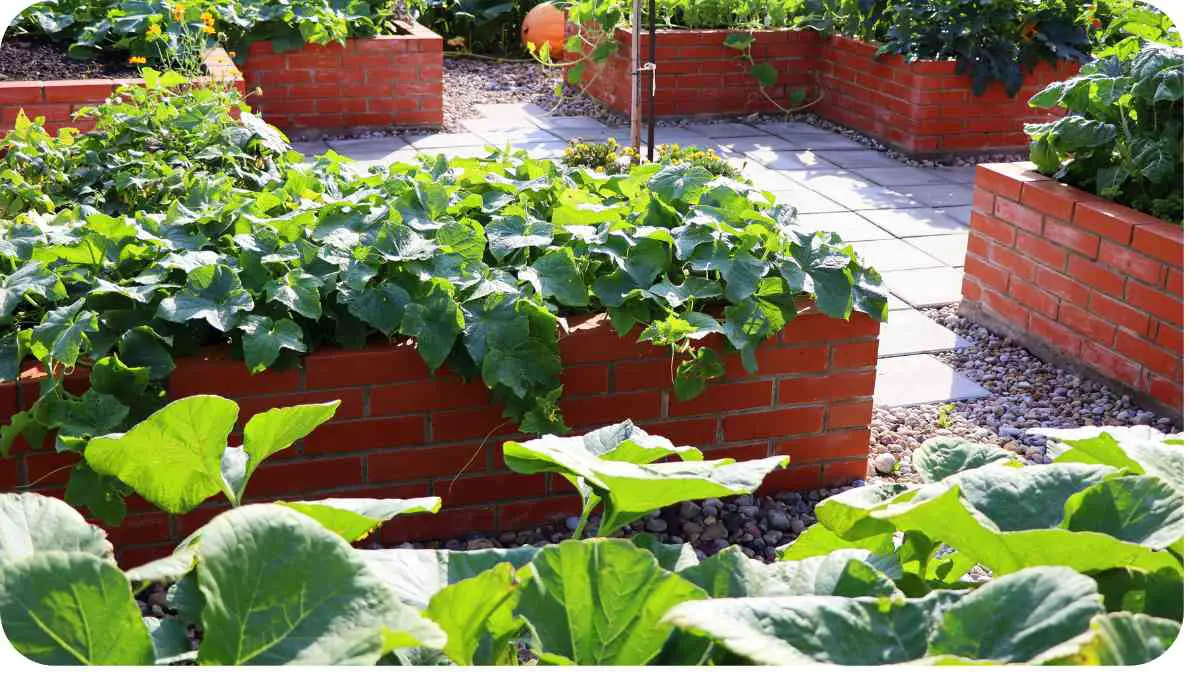
Raised garden beds are a fantastic way to grow a variety of plants, offering better control over soil quality and reducing the strain on your back. However, one common challenge gardeners face is managing drainage.
Poor drainage can lead to waterlogged roots, stunted growth, and ultimately plant death. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to resolve drainage issues in your raised garden beds, ensuring your plants thrive.
| Takeaways |
|---|
| Proper drainage is essential for healthy plant growth. |
| Select a location with good sunlight and a slight slope. |
| Use a well-draining soil mix with topsoil, compost, and perlite/sand. |
| Construct raised beds with rot-resistant materials and proper height. |
| Install drainage systems like perforated pipes or French drains. |
| Add layers of gravel and sand to improve drainage at the base. |
| Incorporate organic matter to enhance soil structure and drainage. |
| Regularly maintain and monitor your raised beds for drainage issues. |
| Test soil drainage periodically to ensure optimal conditions. |
| Avoid common mistakes like overwatering and ignoring soil type. |
Understanding Drainage Issues

What Causes Drainage Problems?
Drainage problems in raised garden beds can be caused by several factors, including:
- Poor Soil Composition: Heavy clay soils retain too much water.
- Inadequate Bed Height: Beds that are too shallow don’t allow for sufficient drainage.
- Improper Bed Construction: Lack of drainage holes or a solid base can trap water.
Enhancing your garden’s drainage is essential for healthy plant growth. Proper water management common issues and fixes can prevent waterlogging, root rot, and other problems, ensuring your plants thrive in optimal conditions.
Signs of Poor Drainage
Recognizing the signs of poor drainage early can save your plants. Look out for:
- Water pooling on the soil surface.
- Soil that remains soggy for days after watering or rain.
- Yellowing leaves and root rot.
The Importance of Proper Drainage
Proper drainage is crucial for healthy plant growth. It prevents root rot, helps plants access the oxygen they need, and allows beneficial soil microorganisms to thrive. Ensuring your raised beds have good drainage can significantly impact the success of your garden.
Selecting the Right Location
Sunlight and Slope
Choosing the right location for your raised bed is the first step in managing drainage. Ensure the site gets plenty of sunlight and has a slight slope to facilitate water runoff.
Proximity to Water Sources
While good drainage is vital, you also need easy access to water. Place your raised bed near a water source, but avoid areas that are prone to flooding.
When dealing with drainage problems in container gardens, it’s crucial to address them promptly to prevent waterlogged soil and root suffocation. Proper drainage promotes healthy plant growth and reduces the risk of fungal diseases and root rot.
Choosing the Best Soil for Drainage

Soil Composition
The ideal soil for raised beds is a mix of:
- Topsoil: Provides essential nutrients.
- Compost: Enhances soil structure and drainage.
- Perlite or Sand: Improves aeration and water movement.
Soil Amendments
Adding organic matter like compost or peat moss can significantly improve soil drainage. These amendments help create a looser, more porous soil structure.
| Soil Component | Benefits for Drainage |
|---|---|
| Topsoil | Nutrient-rich base |
| Compost | Improves structure and water movement |
| Perlite/Sand | Enhances aeration and drainage |
Raised Bed Construction Tips
Materials and Design
Selecting the right materials and design for your raised bed can prevent drainage issues. Opt for rot-resistant wood, bricks, or galvanized metal. Ensure the bed is designed with drainage in mind, including gaps or holes at the bottom.
Shade-loving plants may wilt due to various factors, including insufficient water or poor drainage. By troubleshooting the issues, you can revive your plants and create a thriving garden even in shady areas.
Proper Bed Height
A minimum height of 12 inches is recommended for adequate drainage. Taller beds (18-24 inches) are even better for root development and water management.
Installing a Drainage System
Types of Drainage Systems
Consider installing a drainage system within your raised bed, such as:
- Perforated Pipes: Help direct water away from roots.
- French Drains: Channels water out of the bed.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
- Prepare the Base: Excavate the area and create a slope.
- Add a Gravel Layer: Lay down a few inches of gravel.
- Install Pipes: Place perforated pipes or create a French drain.
- Cover with Fabric: Use landscape fabric to separate soil from gravel.
- Fill with Soil: Add your soil mix, ensuring it’s well-draining.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Prepare Base | Excavate area, create slope |
| Add Gravel | Lay down a few inches of gravel |
| Install Pipes | Place perforated pipes or French drain |
| Cover Fabric | Use landscape fabric over gravel |
| Fill with Soil | Add well-draining soil mix |
Using Gravel and Sand Layers
Benefits of a Gravel Layer
Gravel at the base of your raised bed can significantly improve drainage by creating a barrier that allows excess water to escape.
Proper Layering Techniques
For effective drainage:
- Gravel Layer: Add 2-3 inches of gravel.
- Sand Layer: Add 1-2 inches of coarse sand.
- Soil Mix: Top with your soil mixture.
Incorporating Organic Matter
Benefits of Compost
Compost not only enriches the soil but also enhances drainage by improving soil structure and aeration.
Reviving wilting plants requires identifying the underlying causes and implementing appropriate solutions. Whether it’s adjusting watering habits, improving soil drainage, or providing adequate sunlight, proactive measures can help restore your plants’ health and vitality.
How to Properly Mix Compost
Mix compost thoroughly with your soil. Aim for a ratio of about 1 part compost to 3 parts soil.
Adding Drainage Pipes
Types of Drainage Pipes
- PVC Pipes: Durable and easy to install.
- Flexible Drainage Pipes: Easier to maneuver around bed corners.
Installation Process
- Lay Pipes: Position pipes at the base before adding soil.
- Ensure Slope: Make sure pipes are sloped to allow water flow.
- Cover Pipes: Use landscape fabric to prevent soil from clogging pipes.
Maintaining Proper Drainage
Regular Maintenance Tips
- Check drainage holes for blockages.
- Monitor soil moisture levels.
- Adjust watering practices based on weather conditions.
Seasonal Considerations
Different seasons bring different challenges. In rainy seasons, ensure drainage systems are clear. In dry seasons, avoid overwatering.
Dealing with Excess Water

Creating a French Drain
A French drain is an excellent solution for excess water. Dig a trench, line it with gravel, and place a perforated pipe to direct water away from your garden bed.
Using Rain Barrels
Rain barrels can collect excess rainwater, preventing it from pooling in your raised bed while providing a sustainable water source.
Testing Soil Drainage
Simple Drainage Tests
A basic drainage test involves digging a hole, filling it with water, and observing how long it takes to drain. If water remains after 24 hours, you have a drainage issue.
Interpreting Results
Fast drainage indicates sandy soil, while slow drainage points to clay-heavy soil. Adjust your soil composition accordingly.
| Drainage Test Result | Soil Type | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Fast Drainage | Sandy | Add compost to retain moisture |
| Slow Drainage | Clay-heavy | Add sand and organic matter |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Overwatering
One of the most common mistakes is overwatering. Always check soil moisture before watering.
Ignoring Soil Type
Understanding your soil type is crucial. Tailor your soil mix to improve drainage based on your specific conditions.
Expert Tips and Tricks
Personal Experiences
From my experience, regularly turning the soil and adding organic matter has kept my garden beds thriving. I’ve also found that installing a simple gravel layer at the base can make a world of difference.
Soil compaction can hinder root growth and water absorption, leading to stunted plant growth. Implementing effective strategies to alleviate soil compaction, such as aerating the soil and adding organic matter, promotes healthy root development and enhances overall plant vigor.
Advice from Professional Gardeners
Jane Doe, a professional gardener, emphasizes the importance of testing soil regularly and adjusting watering schedules based on seasonal changes. John Smith recommends using raised beds with removable sides for easy maintenance and inspection.
Conclusion
Managing drainage in raised garden beds is essential for healthy, thriving plants. By understanding the causes of drainage issues, selecting the right soil and location, and implementing effective drainage systems, you can ensure your garden bed provides the ideal environment for your plants. Regular maintenance and proper construction techniques will keep your garden flourishing season after season.
Happy gardening!
Further Reading
For more information on resolving drainage issues in raised garden beds, check out these resources:
- Epic Gardening: Raised Beds Drainage Explore comprehensive tips on ensuring proper drainage in your raised beds to prevent waterlogging and promote healthy plant growth.
- Better Homes & Gardens: Improve Poor Drainage Learn about various techniques and solutions to improve poor drainage in your garden, from soil amendments to structural changes.
- Mazzeo’s Landscaping Supplies: How to Improve Drainage in Your Garden Discover practical advice on enhancing garden drainage, including the use of materials like gravel and sand to prevent water accumulation.
FAQs
What are the common signs of drainage issues in raised garden beds?
Common signs include water pooling on the surface, soil remaining soggy for days, and plants showing symptoms of root rot, such as yellowing leaves and stunted growth.
How can I improve drainage in my existing raised garden bed?
You can improve drainage by adding a layer of gravel or sand at the base, incorporating organic matter like compost, and ensuring the soil mix is well-draining. Installing drainage pipes or creating a French drain can also help.
Why is soil composition important for drainage in raised beds?
Soil composition is crucial because different soil types have varying drainage capabilities. A well-draining soil mix usually contains a balance of topsoil, compost, and perlite or sand to ensure excess water can move through the soil without causing root rot.
What materials are best for constructing raised garden beds to enhance drainage?
Materials like rot-resistant wood, bricks, and galvanized metal are excellent choices for constructing raised beds. Ensure the design includes gaps or holes at the bottom to facilitate water drainage.
How often should I check the drainage of my raised garden bed?
It’s a good practice to check the drainage regularly, especially after heavy rainfall or watering. Conducting a simple drainage test periodically can help identify and address any issues before they affect plant health.

Hi! My name is Hellen James, and I’m here to help you with your home-maintenance needs. Whether it’s building a better yard or just trying to fix a garden—I can show you how.