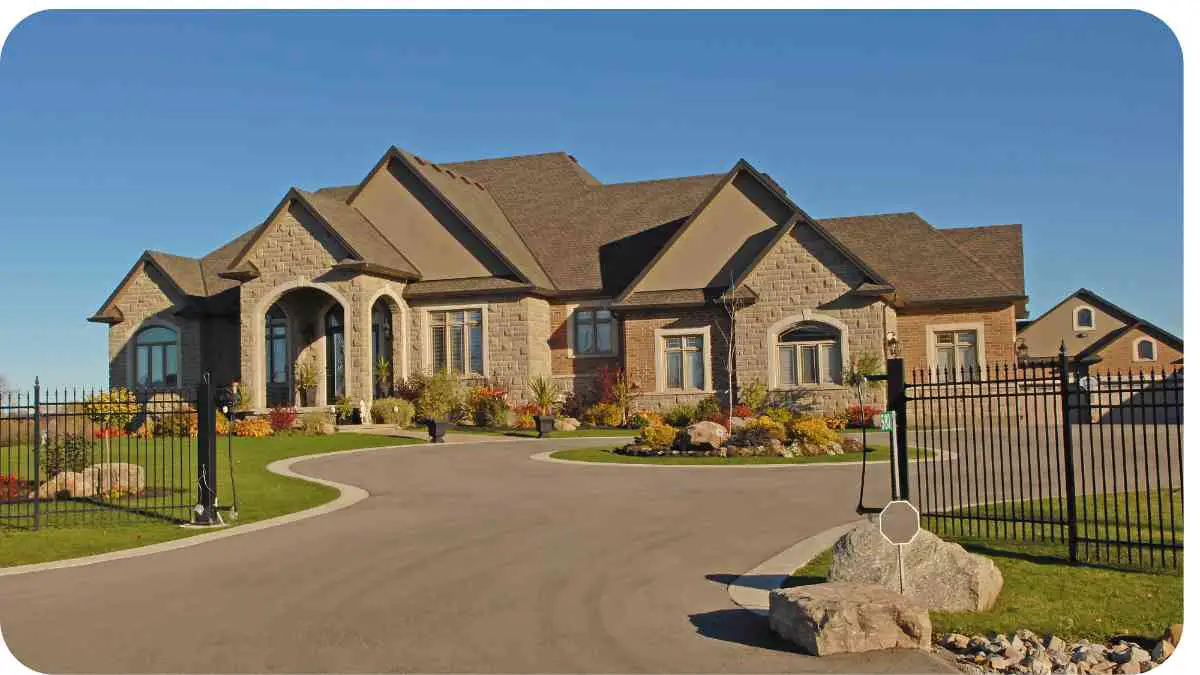
Are you tired of parking on the street or dealing with a cramped and narrow driveway? Building a driveway in your front yard can be a great solution, but it’s not a decision to be taken lightly.
Before you start digging and pouring concrete, there are several factors to consider, including local regulations, environmental impact, and safety considerations.
| Takeaway |
|---|
| Consider local regulations and zoning laws before building a driveway |
| Environmental impact and safety considerations are crucial when building a driveway |
| Choose the right materials for your driveway, such as asphalt, concrete, or gravel |
| Proper maintenance and upkeep are essential to extend the life of your driveway |
| Building a driveway can increase your property’s value and appeal |
Importance of Considering Local Regulations
Before you begin building your driveway, it’s essential to research and understand the local regulations and zoning laws in your area. These laws can vary significantly from one region to another, and failing to comply with them can result in costly fines, penalties, and even the removal of your driveway.
Creating a drought-resistant front yard involves smart landscaping choices and water-saving techniques. With proper planning and construction tips, you can build a driveway that complements your water-wise landscape.
Factors to Consider Before Building a Driveway
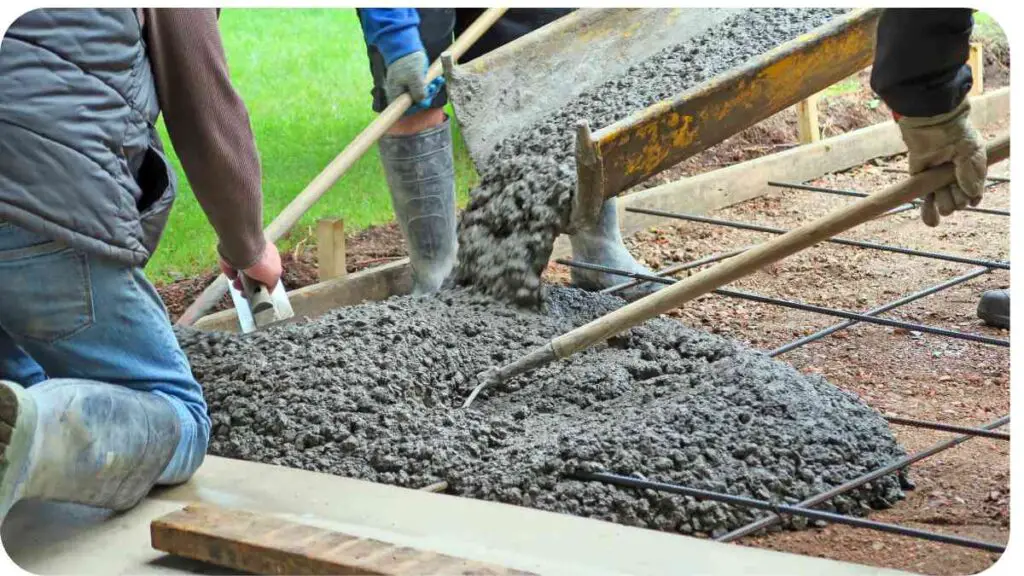

Building a driveway is a significant investment, and it’s crucial to consider several factors before breaking ground. These include:
- Local zoning laws and regulations
- Environmental impact and safety considerations
- Driveway design and layout options
- Choosing the right materials for your driveway
- Permits and inspections
- Budgeting and cost considerations
- Maintenance and upkeep
Let’s dive deeper into each of these factors and explore what you need to know before building a driveway in your front yard.
Understanding Local Zoning Laws and Regulations
Local zoning laws and regulations can significantly impact your ability to build a driveway in your front yard. These laws dictate how property can be used, including the size and location of driveways.
Wondering about building structures in your front yard? Learn about regulations and considerations for front garden structures like driveways and garages to ensure compliance and feasibility.
Researching Local Ordinances and Codes
To determine what’s allowed in your area, you’ll need to research local ordinances and codes. You can start by:
- Visiting your local government’s website or planning department
- Reviewing local zoning laws and regulations
- Consulting with a local attorney or zoning expert
Types of Zoning Laws Affecting Driveway Construction
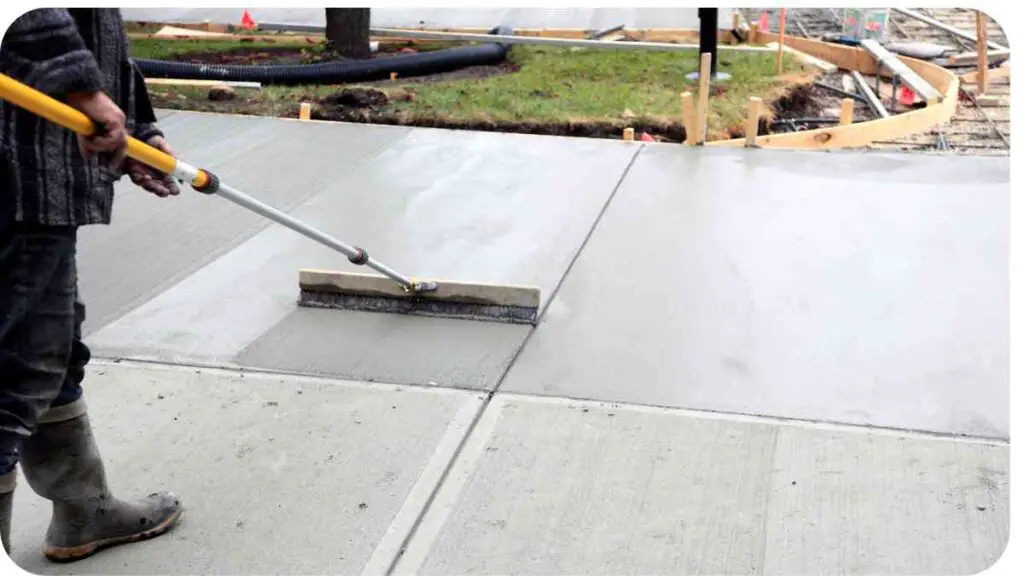

Zoning laws can affect driveway construction in several ways, including:
- Setback requirements: The distance between your driveway and the street or adjacent properties
- Lot coverage: The percentage of your property that can be covered by impervious surfaces like driveways
- Driveway width and length: The maximum size of your driveway
Table: Common Zoning Laws Related to Driveways
| Zoning Law | Description |
| Setback Requirements | The distance between your driveway and the street or adjacent properties |
| Lot Coverage | The percentage of your property that can be covered by impervious surfaces like driveways |
| Driveway Width and Length | The maximum size of your driveway |
| Environmental Impact | Regulations related to stormwater management, drainage, and environmental impact |
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
When building a driveway, it’s essential to consider the environmental impact and safety implications of your project. These factors can have a significant impact on your property, the surrounding environment, and the safety of pedestrians and vehicles.
Transforming a sloping front yard into a beautiful landscape requires strategic planning and creativity. Explore landscaping ideas to tackle challenges like driveway construction on uneven terrain.
Environmental Concerns: Drainage and Water Runoff
One of the primary environmental concerns related to driveway construction is drainage and water runoff. When you build a driveway, you’re creating an impervious surface that can alter the natural flow of water on your property. This can lead to:
- Erosion and sedimentation
- Water pollution
- Increased risk of flooding
To mitigate these risks, you can implement strategies like:
- Installing a drainage system or rain garden
- Using permeable pavers or materials
- Creating a swale or bioswale to manage water runoff
Safety Considerations: Pedestrian and Vehicle Traffic
Driveways can also pose safety risks to pedestrians and vehicles, particularly if they’re not designed or constructed with safety in mind. Some safety considerations include:
- Pedestrian visibility and access
- Vehicle speed and traffic flow
- Conflict points between pedestrians, cyclists, and vehicles
To ensure safety, you can implement measures like:
- Installing pedestrian crossings or traffic calming features
- Implementing speed bumps or traffic circles
- Improving lighting and visibility
Table: Environmental and Safety Factors to Consider
| Factor | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
| Drainage and Water Runoff | Altered water flow, erosion, and pollution | Drainage systems, permeable pavers, rain gardens |
| Pedestrian Visibility | Reduced visibility and access | Pedestrian crossings, traffic calming features |
| Vehicle Speed and Traffic Flow | Increased risk of accidents | Speed bumps, traffic circles, improved lighting |
Driveway Design and Layout Options
When designing your driveway, you have several layout options to consider. These can affect the functionality, safety, and aesthetics of your driveway.
Maximize your front yard space for outdoor enjoyment with these creative ideas. Discover ways to utilize your front yard effectively, whether for a driveway, garden, or relaxation area.
Straight, Curved, or Circular Driveway Designs
Driveway design can be categorized into three main types:
- Straight driveways: Simple and functional, but may not be aesthetically pleasing
- Curved driveways: More visually appealing, but can be more challenging to navigate
- Circular driveways: Provide a sense of grandeur, but may require more space and materials
One-Way or Two-Way Traffic Flow
You’ll also need to decide on the traffic flow of your driveway. One-way traffic flow can be more efficient, but may not be suitable for larger properties or higher traffic volumes.
Table: Driveway Design and Layout Options
| Design Option | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Straight | Simple and functional | Easy to navigate, cost-effective | Aesthetically unappealing |
| Curved | Visually appealing | More attractive, can increase property value | More challenging to navigate |
| Circular | Grand and impressive | Can increase property value, provides a sense of grandeur | Requires more space and materials |
Choosing the Right Materials for Your Driveway
When building a driveway, the materials you choose can significantly impact the durability, maintenance, and overall appearance of your driveway. Here are some common materials to consider:
Asphalt, Concrete, or Gravel: Which is Best?
The three most common materials for driveways are asphalt, concrete, and gravel. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Asphalt: Cost-effective, easy to install, and relatively low maintenance. However, it can be prone to cracking and may require frequent resurfacing.
- Concrete: Durable, long-lasting, and can be stamped or stained for aesthetic appeal. However, it can be expensive, and installation can be labor-intensive.
- Gravel: Affordable, easy to install, and allows for good drainage. However, it can be prone to rutting and may require frequent replenishment.
Table: Comparison of Driveway Materials
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Cost |
| Asphalt | Cost-effective, easy to install, low maintenance | Prone to cracking, frequent resurfacing | $2 – $5 per sq ft |
| Concrete | Durable, long-lasting, aesthetic appeal | Expensive, labor-intensive installation | $5 – $10 per sq ft |
| Gravel | Affordable, easy to install, good drainage | Prone to rutting, frequent replenishment | $1 – $3 per sq ft |
Permits and Inspections: What to Expect
Before you begin building your driveway, you’ll need to obtain the necessary permits and approvals from your local government. This can include:
- Building permits
- Zoning permits
- Environmental permits
- Inspections
Planning to build a driveway? Understand the costs involved, including expenses like resodding. Learn about front lawn resodding costs after construction projects like driveway installation to maintain your front yard’s appeal.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Approvals
To obtain the necessary permits, you’ll need to:
- Submit plans and applications to your local government
- Pay applicable fees
- Wait for approval and issuance of permits
Scheduling Inspections and Passing Muster
Once you’ve obtained the necessary permits, you’ll need to schedule inspections to ensure compliance with local regulations. This can include:
- Pre-construction inspections
- Mid-construction inspections
- Final inspections
Table: Permit and Inspection Requirements
| Permit/Inspection | Description | Timeline |
| Building Permit | Approval for construction | 1-2 weeks |
| Zoning Permit | Approval for zoning compliance | 1-2 weeks |
| Environmental Permit | Approval for environmental compliance | 2-4 weeks |
| Pre-construction Inspection | Inspection before construction begins | 1-2 days |
| Mid-construction Inspection | Inspection during construction | 1-2 days |
| Final Inspection | Inspection after construction is complete | 1-2 days |
Driveway Construction Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Building a driveway can be a complex process, but breaking it down into smaller steps can make it more manageable. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the construction process:
Step 1: Site Preparation and Excavation
Before you begin building your driveway, you’ll need to prepare the site. This includes:
- Clearing the area of debris and vegetation
- Grading the soil to ensure a level surface
- Excavating the area to a depth of 8-10 inches
Step 2: Laying the Foundation and Base Course
Once the site is prepared, you’ll need to lay the foundation and base course. This includes:
- Laying a layer of compacted gravel or crushed stone
- Installing a geotextile fabric to prevent weed growth and stabilize the soil
- Laying a layer of compacted asphalt or concrete
Step 3: Installing the Driveway Surface
With the foundation and base course in place, you can now install the driveway surface. This includes:
- Laying a layer of asphalt or concrete
- Installing a layer of compacted gravel or crushed stone
- Finishing the surface with a sealcoat or pavement sealant
Table: Driveway Construction Process Timeline
| Step | Description | Timeline |
| Site Preparation | Clearing, grading, and excavating the site | 1-2 days |
| Foundation and Base Course | Laying the foundation and base course | 2-3 days |
| Driveway Surface | Installing the driveway surface | 2-3 days |
| Final Inspection | Final inspection and completion of the driveway | 1-2 days |
Budgeting and Cost Considerations
Building a driveway can be a significant investment, and it’s essential to budget and plan accordingly. Here are some cost considerations to keep in mind:
- Materials: Asphalt, concrete, gravel, and other materials can vary in cost depending on the supplier and location.
- Labor: Hiring a contractor or laborer can add to the overall cost of the project.
- Equipment: Renting or purchasing equipment, such as excavators or pavers, can also impact the cost.
Table: Estimated Costs for Driveway Construction
| Material/Labor | Cost |
| Asphalt | $2 – $5 per sq ft |
| Concrete | $5 – $10 per sq ft |
| Gravel | $1 – $3 per sq ft |
| Labor | $500 – $1,000 per day |
| Equipment | $500 – $1,000 per day |
Maintenance and Upkeep: Keeping Your Driveway in Good Condition

After building your driveway, it’s essential to maintain and upkeep it to ensure it remains in good condition. Here are some tips to help you keep your driveway looking its best:
Regular Cleaning and Debris Removal
Regularly cleaning your driveway can help prevent damage and maintain its appearance. This includes:
- Sweeping or blowing leaves and debris off the driveway
- Washing the driveway with soap and water to remove dirt and stains
- Removing oil and grease stains with a degreaser
Crack Sealing and Repair
Cracks in your driveway can lead to more significant problems if left unrepaired. Here are some tips for crack sealing and repair:
- Seal cracks as soon as possible to prevent water from seeping in
- Use a crack sealant specifically designed for driveways
- Fill potholes and repair damaged areas with a patching material
Table: Driveway Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency |
| Cleaning and Debris Removal | Weekly/Bi-Weekly |
| Crack Sealing and Repair | As needed |
| Sealcoating | Every 2-3 years |
| Inspections | Quarterly |
Sealcoating: Protecting Your Driveway from the Elements
Sealcoating is a protective layer applied to your driveway to protect it from the elements. Here are some benefits of sealcoating:
- Protects against water, UV rays, and extreme temperatures
- Reduces maintenance and repair costs
- Enhances the appearance of your driveway
Inspections: Identifying Potential Issues
Regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they become major problems. Here are some things to look for during an inspection:
- Cracks and damage
- Drainage issues
- Vegetation growth
- Potholes and uneven surfaces
Conclusion
Building a driveway can be a significant investment, but with proper planning, construction, and maintenance, it can last for years to come. Remember to consider local regulations, environmental impact, and safety considerations before building your driveway. By following these tips and guidelines, you can create a beautiful and functional driveway that enhances your property’s value and appeal.
Further Reading
- Can I Turn My Front Garden into a Driveway? – Griggs Homes
- Can I Turn My Front Garden into a Driveway? – Garden Gates Direct
FAQs
Do I need planning permission to pave my front garden?
You do not need planning permission to pave your front garden, but there are certain guidelines to follow. The surface must be permeable, and if the area is more than 5 metres squared, you may need planning permission.
What is a dropped kerb, and do I need planning permission for it?
A dropped kerb is a modification to the footway that involves lowering the kerb to create a driveway. Yes, you need planning permission from the local council to drop a kerb, and the council will assign a contractor to carry out the work.
Can I pave my front garden if I live in a conservation area?
If you live in a conservation area, you may face additional challenges when trying to pave your front garden. You will need to ensure that the driveway is in keeping with the style and architectural features of the surrounding area.
How much value can a driveway add to my property?
A driveway can add 5-10% to the value of your property, depending on the location and other factors.
Do I need to consider the width of my driveway?
Yes, you need to ensure that your driveway is wide enough to accommodate your vehicle(s) comfortably, with a minimum width of 2.4 metres by 4.8 metres.

Hi! My name is Hellen James, and I’m here to help you with your home-maintenance needs. Whether it’s building a better yard or just trying to fix a garden—I can show you how.