Maintaining a lush, green lawn requires more than just regular mowing and watering. Lawn thatch buildup can hinder the growth of your grass and create a host of problems if left unchecked. Understanding the causes and solutions for thatch accumulation is essential for achieving a healthy and vibrant lawn.
| Takeaways |
|---|
| Thatch buildup can hinder lawn health. |
| Proper maintenance prevents thatch buildup. |
| Identification is key to addressing thatch. |
| Effective treatment restores lawn vitality. |
| Regular care ensures long-term lawn health. |
2. What is Lawn Thatch?
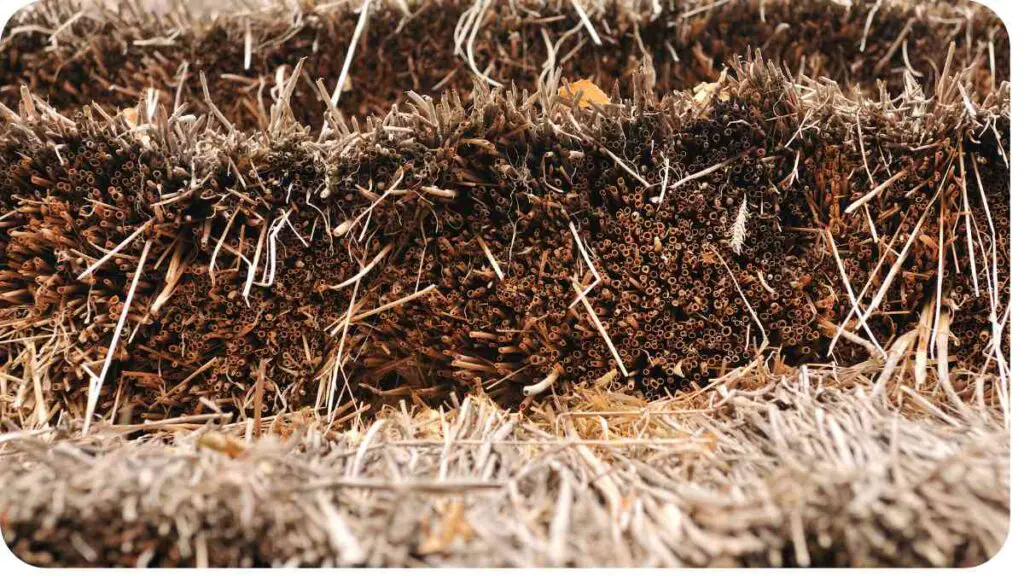

Before delving into the causes and solutions, let’s define what exactly lawn thatch is. Thatch is a layer of dead grass, roots, and organic debris that accumulates between the soil surface and the green vegetation of your lawn. While some thatch is natural and beneficial, excessive buildup can impede the growth of your grass and lead to various issues.
Adjusting lawn sprinkler heads ensures optimal watering coverage, crucial for a healthy lawn. Proper adjustment prevents under or over-watering, promoting lush greenery. Learn expert techniques for adjusting lawn sprinkler heads for a vibrant lawn.
Table: Components of Lawn Thatch
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Dead Grass | Grass clippings and stems that have decomposed over time |
| Roots | Decomposed root material that forms part of the thatch |
| Organic Debris | Leaves, twigs, and other organic matter |
Now that we’ve clarified what lawn thatch is, let’s explore the factors that contribute to its buildup.
3. Causes of Lawn Thatch Buildup
Several factors can contribute to the accumulation of thatch on your lawn. Understanding these causes is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies.
3.1 Lack of Aeration
Aeration plays a vital role in preventing thatch buildup by facilitating the decomposition of organic matter. When soil becomes compacted, it restricts the flow of air, water, and nutrients, leading to the accumulation of thatch. Regular aeration helps alleviate compaction and promotes a healthy soil environment.
Table: Benefits of Lawn Aeration
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Soil Structure | Loosens compacted soil, allowing roots to penetrate more easily |
| Enhanced Nutrient Absorption | Facilitates the uptake of essential nutrients by grass roots |
| Increased Water Infiltration | Improves water penetration and reduces surface runoff |
| Promotion of Microbial Activity | Encourages beneficial soil microbes, aiding in organic matter decomposition |
3.2 Overfertilization
While fertilization is essential for promoting healthy grass growth, excessive use of fertilizers can contribute to thatch accumulation. When grass receives an abundance of nutrients, it grows vigorously, leading to an accumulation of dead organic matter. It’s crucial to follow proper fertilization practices and avoid overapplication of fertilizers to prevent thatch buildup.
Maintaining sharp lawn mower blades is key to a neat and healthy lawn. Blunt blades can tear grass, leading to thatch buildup and disease susceptibility. Discover expert tips for adjusting lawn mower blades to ensure pristine lawn care.
Table: Guidelines for Proper Fertilization
| Fertilization Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Testing | Conduct soil tests to determine nutrient deficiencies and apply fertilizers accordingly |
| Slow-Release Fertilizers | Use slow-release fertilizers to provide a steady supply of nutrients over an extended period |
| Proper Application Rates | Follow manufacturer recommendations for application rates and avoid excessive fertilizer usage |
| Timing of Application | Apply fertilizers during periods of active growth and avoid fertilizing dormant or stressed grass |
3.3 Excessive Irrigation
Overwatering your lawn can contribute to thatch buildup by promoting rapid grass growth and impeding the decomposition of organic matter. When soil is consistently saturated with water, microbial activity slows down, allowing thatch to accumulate more quickly. It’s essential to practice proper irrigation techniques to maintain optimal soil moisture levels and prevent excessive thatch accumulation.
Proper adjustment of the lawn mower deck is essential for an even and uniform cut. Uneven deck settings can result in scalping or missed spots, affecting the overall appearance of your lawn. Explore expert advice on adjusting lawn mower deck for impeccable lawn maintenance.
Table: Tips for Proper Lawn Irrigation
| Irrigation Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Deep and Infrequent Watering | Water deeply and less frequently to encourage deep root growth and reduce surface thatch accumulation |
| Time of Day | Water in the early morning to minimize evaporation and fungal diseases, and avoid watering at night |
| Use of Irrigation Timers | Install irrigation timers to ensure consistent watering schedules and prevent overwatering |
| Monitor Soil Moisture Levels | Use a moisture meter or conduct a soil moisture test to determine when watering is necessary |
4. Effects of Thatch on Your Lawn

Thatch accumulation can negatively impact the health and appearance of your lawn in several ways. Understanding these effects is essential for recognizing and addressing thatch-related issues.
4.1 Compromised Nutrient Absorption
Excessive thatch can create a barrier that prevents nutrients from reaching the roots of your grass. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies and hinder the overall health and growth of your lawn. By addressing thatch buildup, you can ensure that your grass receives the essential nutrients it needs to thrive.
Table: Signs of Nutrient Deficiencies in Grass
| Nutrient Deficiency | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Yellowing of leaves, stunted growth |
| Phosphorus | Purplish discoloration of leaves, weak root development |
| Potassium | Brown or scorched leaf margins, poor drought tolerance |
4.2 Water Retention Issues
Thatch buildup can also affect the water retention capacity of your soil. Excessive thatch acts as a sponge, absorbing and holding onto moisture, which can lead to waterlogging and root suffocation. This can result in shallow root systems and increased susceptibility to drought stress. By addressing thatch accumulation, you can improve water penetration and distribution within the soil, promoting healthier root growth.
Regulating the lawn mower governor optimizes engine performance and fuel efficiency. Incorrect governor settings can lead to engine strain or poor cutting performance. Master the art of adjusting lawn mower governor for a smooth and efficient mowing experience.
Table: Symptoms of Waterlogged Soil
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Standing Water | Puddles or pools of water that remain on the surface of the lawn after watering |
| Soggy Soil Texture | Soil feels excessively wet and muddy to the touch |
| Wilting and Yellowing | Signs of overwatering and root suffocation in grass plants |
| Foul Odor | Presence of anaerobic bacteria in waterlogged soil, emitting a rotten smell |
4.3 Pest and Disease Infestation
Thatch buildup creates an ideal habitat for pests and disease pathogens to thrive. The dense, moist environment provides shelter and nutrients for harmful organisms, increasing the risk of infestation and disease outbreaks in your lawn. By reducing thatch accumulation through proper maintenance practices, you can mitigate the risk of pest and disease problems and promote a healthier ecosystem in your yard.
Table: Common Lawn Pests and Diseases Associated with Thatch Buildup
| Pest/Disease | Description |
|---|---|
| White Grubs | Larvae of beetles that feed on grass roots, causing brown patches and wilting |
| Dollar Spot | Fungal disease characterized by small, circular patches of brown or straw-colored grass |
| Chafer Beetles | Adults feed on grass foliage, while larvae (grubs) feed on grassroots, leading to thinning and browning |
| Pythium Blight | Fungal disease causing rapid blighting and wilting of grass, often in areas with poor drainage or excess thatch |
5. Identifying Thatch Buildup
Recognizing the signs of thatch accumulation is the first step towards addressing this issue and restoring the health of your lawn. Let’s explore some methods for identifying thatch buildup.
5.1 Visual Inspection
One of the simplest ways to assess thatch buildup is through visual inspection. Take a close look at your lawn and observe the layer of organic material between the soil and the grass blades. If this layer appears thick and spongy, it’s likely thatch buildup is present.
Soil compaction can hinder root growth and nutrient absorption, affecting overall lawn health. Addressing soil compaction issues is crucial for promoting lush, green lawns. Explore valuable tips for dealing with soil compaction and fostering healthy turf.
Table: Signs of Thatch Buildup During Visual Inspection
| Observation | Description |
|---|---|
| Layer Thickness | Measure the thickness of the thatch layer using a ruler or probe |
| Sponginess | Press down on the turfgrass and assess the resilience and sponginess of the thatch |
| Color | Thatch layer may appear brownish or straw-colored compared to underlying soil |
5.2 Performing a Thatch Test
In addition to visual inspection, you can perform a simple thatch test to gauge the extent of buildup in your lawn. Here’s how to conduct a thatch test:
- Use a shovel or a hand trowel to cut a small section of turfgrass, approximately 6 inches square, from your lawn.
- Examine the cross-section of the turfgrass, paying close attention to the layer between the soil and the base of the grass blades.
- Measure the thickness of the thatch layer using a ruler or calipers. Thatch layers greater than 1/2 inch thick may require remedial action.
Performing a thatch test allows you to accurately assess the severity of thatch buildup and determine the appropriate course of action to address it.
Table: Steps for Conducting a Thatch Test
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Select Test Area | Choose a representative area of your lawn to conduct the test, preferably with visible thatch |
| Cut Turfgrass | Use a shovel or trowel to cut a small section of turfgrass, ensuring it is approximately 6 inches square |
| Examine Cross-Section | Inspect the cross-section of the turfgrass, focusing on the layer between the soil and grass blades |
| Measure Thatch Thickness | Use a ruler or calipers to measure the thickness of the thatch layer in inches |
6. Preventing Thatch Buildup
Prevention is key when it comes to managing thatch buildup in your lawn. By adopting proactive maintenance practices, you can minimize the accumulation of thatch and promote a healthier lawn ecosystem.
6.1 Proper Mowing Techniques

Maintaining the correct mowing height and frequency is essential for preventing thatch buildup. Follow these guidelines for proper mowing:
- Mow at the Right Height: Adjust your lawn mower to the recommended mowing height for your grass species. Mowing too low can stress the grass and promote thatch accumulation.
- Regular Mowing Schedule: Mow your lawn regularly to prevent grass from becoming overgrown and producing excessive thatch.
Table: Recommended Mowing Heights for Common Grass Species
| Grass Species | Mowing Height (inches) |
|---|---|
| Bermuda Grass | 0.5 – 1.5 |
| Kentucky Bluegrass | 1.5 – 2.5 |
| Zoysia Grass | 0.5 – 2 |
| Fescue Grass | 2 – 3 |
6.2 Regular Aeration
Aeration is a critical component of lawn care that helps alleviate soil compaction and promote healthy root growth. By aerating your lawn regularly, you can improve soil drainage and enhance the decomposition of organic matter, reducing the likelihood of thatch buildup.
Table: Benefits of Regular Lawn Aeration
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Soil Structure | Loosens compacted soil, allowing roots to penetrate more easily |
| Enhanced Nutrient Absorption | Facilitates the uptake of essential nutrients by grass roots |
| Increased Water Infiltration | Improves water penetration and reduces surface runoff |
| Promotion of Microbial Activity | Encourages beneficial soil microbes, aiding in organic matter decomposition |
6.3 Balanced Fertilization
Proper fertilization practices are essential for maintaining a healthy lawn while minimizing thatch accumulation. Follow these guidelines for balanced fertilization:
- Soil Testing: Conduct soil tests to determine nutrient deficiencies and apply fertilizers accordingly. Avoid excessive fertilization, as it can contribute to thatch buildup.
- Slow-Release Fertilizers: Use slow-release fertilizers to provide a steady supply of nutrients to your grass over an extended period, reducing the risk of thatch accumulation.
- Timing of Application: Apply fertilizers during periods of active growth and avoid fertilizing dormant or stressed grass, as excess nutrients can contribute to thatch buildup.
Table: Guidelines for Balanced Fertilization
| Fertilization Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Testing | Conduct soil tests to determine nutrient deficiencies and apply fertilizers accordingly |
| Slow-Release Fertilizers | Use slow-release fertilizers to provide a steady supply of nutrients over an extended period |
| Proper Application Rates | Follow manufacturer recommendations for application rates and avoid excessive fertilizer usage |
| Timing of Application | Apply fertilizers during periods of active growth and avoid fertilizing dormant or stressed grass |
7. Treating Existing Thatch
If you’ve already noticed significant thatch buildup in your lawn, don’t worry! There are several methods for treating existing thatch and restoring the health of your turf.
7.1 Vertical Mowing
Vertical mowing, also known as verticutting, is a process that involves cutting through the thatch layer and into the soil to promote decomposition and removal of organic matter. This mechanical dethatching method can be effective for addressing moderate to severe thatch buildup.
Table: Steps for Vertical Mowing
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Adjust Mower Depth | Set the mower blades to penetrate the thatch layer and reach the soil surface |
| Vertical Mowing Pattern | Mow in overlapping passes across the lawn, ensuring thorough coverage of the affected areas |
| Post-Mowing Cleanup | Remove debris and thatch material from the lawn surface to prevent smothering of grass |
7.2 Dethatching
Dethatching involves the removal of thatch from the lawn using specialized equipment such as a dethatching rake or power dethatcher. This process helps to mechanically break up the thatch layer and remove accumulated organic matter, promoting a healthier turfgrass environment.
Table: Steps for Dethatching
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Select Dethatching Equipment | Choose a dethatching rake or power dethatcher suitable for your lawn size and conditions |
| Thoroughly Dethatch | Use the equipment to remove thatch from the lawn surface, focusing on affected areas |
| Post-Dethatching Cleanup | Rake up and remove the loosened thatch material from the lawn surface |
7.3 Topdressing
Topdressing involves applying a thin layer of compost, sand, or a mixture of both to the surface of the lawn. This helps introduce beneficial microorganisms to the soil, enhance soil structure, and encourage decomposition of thatch. Topdressing can be particularly effective in conjunction with other dethatching methods.
Table: Steps for Topdressing
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Prepare Topdressing Material | Choose a suitable topdressing material such as compost or sand |
| Apply Topdressing | Spread the topdressing material evenly across the lawn surface, targeting areas with heavy thatch buildup |
| Work Topdressing into Thatch | Use a rake or broom to work the topdressing material into the thatch layer and soil surface |
| Water and Monitor | Water the lawn thoroughly after topdressing to promote integration of the material into the soil. Monitor for improvements in thatch decomposition over time |
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing lawn thatch buildup is crucial for maintaining a lush and healthy lawn. By understanding the causes of thatch accumulation and implementing effective prevention and treatment strategies, you can promote optimal turfgrass growth and minimize the risk of issues associated with excess thatch.
Remember to regularly inspect your lawn for signs of thatch buildup, perform necessary tests to assess its severity, and take proactive measures to address the problem. Whether it’s through proper mowing techniques, regular aeration, balanced fertilization, or targeted dethatching methods, there are numerous approaches to managing thatch buildup and ensuring the overall health and vitality of your lawn.
By prioritizing thatch management as part of your lawn care routine, you can enjoy a beautiful and resilient lawn that enhances the aesthetic appeal of your outdoor space and provides a welcoming environment for outdoor activities and relaxation.
Further Reading
- Davey: Insect & Disease Resource Center – Thatch: Explore comprehensive information on thatch management, including causes, effects, and treatment methods.
- Penn State Extension: Managing Thatch in Lawns: Learn practical tips and techniques for effectively managing thatch buildup in your lawn.
- LawnMaster: Thatch Advice Centre: Access expert advice and guidance on dealing with thatch issues in your lawn.
FAQs
What is thatch and why does it accumulate in lawns?
Thatch is a layer of dead grass, roots, and organic debris that accumulates between the soil surface and the green vegetation of your lawn. It accumulates due to factors such as incomplete decomposition of organic matter, excessive fertilization, and compacted soil.
How does thatch affect the health of my lawn?
Excessive thatch buildup can hinder the growth of your grass by creating a barrier that prevents nutrients, water, and air from reaching the roots. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies, water retention issues, and increased susceptibility to pest and disease infestation.
How can I identify thatch buildup in my lawn?
You can identify thatch buildup through visual inspection and by performing a thatch test. Look for a thick layer of spongy material between the soil and grass blades, and measure the thickness of the thatch layer using a ruler or calipers.
What are some preventative measures for minimizing thatch accumulation?
Proper mowing techniques, regular aeration, and balanced fertilization are key preventative measures for minimizing thatch accumulation. Mow at the right height, aerate your lawn regularly to alleviate soil compaction, and avoid overfertilization to prevent excessive thatch buildup.
What are effective treatments for existing thatch buildup?
Vertical mowing, dethatching, and topdressing are effective treatments for existing thatch buildup. These methods help to mechanically break up the thatch layer, promote decomposition of organic matter, and improve soil structure for healthier turfgrass growth.

Hi! My name is Hellen James, and I’m here to help you with your home-maintenance needs. Whether it’s building a better yard or just trying to fix a garden—I can show you how.